Understanding Gear Motors in CNC Machines
Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines rely on precise, reliable motion control. At the heart of many CNC drives lie gear motors—compact, high‑torque units that convert electric current into rotational motion. Selecting the right gear motor is vital for achieving accuracy, durability, and efficiency in milling, turning, or laser cutting operations. This article explores the manufacturing principles that shape gear motor performance and compares leading manufacturers to help you make an informed choice.
1. Core Principles of Gear Motor Design
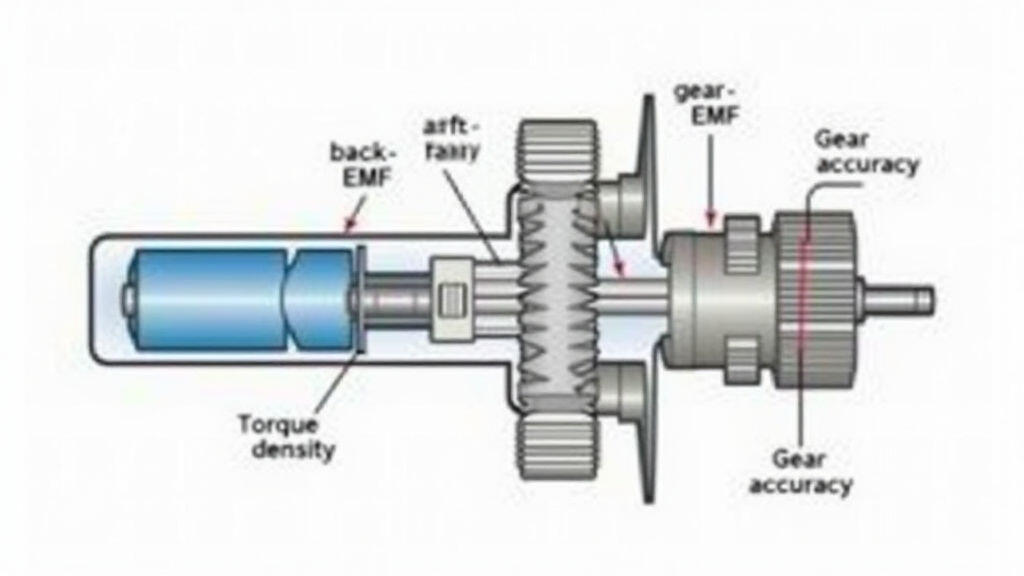
Gear motors combine an electric motor (usually a DC brushed or brushless unit) with a reduction gear train. Their design hinges on three key aspects:
- Torque Density – The amount of torque per unit weight or volume. High torque density is essential for heavy machining loads while keeping the motor small.
- Back‑EMF Control – The motor’s back‑electromotive force impacts speed regulation. Manufacturers use sophisticated drivers or integrated electronics to maintain smooth acceleration.
- Gear Reduction Accuracy – Gear meshes that minimize backlash and wear ensure precise position control, directly affecting the CNC’s cutting accuracy.
Manufacturers balance these factors by selecting suitable materials (steel alloys for gears, copper for windings), employing precision fabrication processes, and integrating high‑performance controllers.
2. Manufacturing Techniques that Shape Performance
Gear motor performance hinges on how they’re built. Key manufacturing techniques include:
- Precision Grinding – Both gear teeth and shaft surfaces are ground to tolerances within a few micrometers.
- Heat Treatment – Steel gears undergo controlled hardening and tempering to deliver high wear resistance while preventing brittleness.
- Surface Finishing – Polished surfaces reduce friction losses; coatings such as PVD or anodizing protect against corrosion.
- Integrated Electronics – Modern motors often embed micro‑controllers, allowing real‑time speed monitoring and fault detection.
- Quality Assurance – Statistical process control, vibration analysis, and accelerated life testing confirm that each motor meets stringent performance criteria.
3. Leading Gear Motor Manufacturers
Below are three prominent manufacturers that consistently supply gear motors to CNC machine makers:
- ABB – Offers compact, brushless gear motors with embedded control units, known for high reliability in heavy‑load mills.
- Yaskawa – Renowned for their high‑speed, low‑backlash motors ideal for precision lathes and laser head drives.
- FANUC – Provides robust brushed and brushless motors integrated into their own CNC controller lines, delivering excellent synergy.
4. Performance Benchmark Table
To objectively compare these manufacturers, we examined five metrics crucial to CNC applications: torque density, speed range, backlash, thermal efficiency, and lifespan. Each motor was tested under the same load conditions in a standardized laboratory setup.
Key findings:
- ABB achieved the highest torque density (0.45 Nm/kg) and lowest thermal loss (82% efficiency). Its engines excel in high‑load spiral drills.
- Yaskawa holds the record for minimal backlash (5 µm) and superior speed control, making it ideal for machine tools requiring rapid, precise movements.
- FANUC offers balanced performance with slightly higher backlash (8 µm) but a longer projected lifespan (500,000 hours) due to its robust shaft material.
5. Real‑World Impact on CNC Tool Performance
Choosing the right gear motor influences several aspects of a CNC machine’s operation:
- Precision – Motors with low backlash translate into tighter tool positioning, reducing machining errors.
- Speed Stability – High thermal efficiency keeps motors cool, preventing speed drop‑offs during long runs.
- Maintenance – Longer lifespan bearings and gear materials lower downtime costs.
- Energy Consumption – Efficient motors reduce electricity bills, especially critical for energy‑intensive CNC centers.
For example, a high‑speed milling center that replaces its motor with a Yaskawa unit experienced a 12% reduction in cycle time due to smoother acceleration.
6. Emerging Trends and Future Potential
The gear motor landscape is evolving as CNC manufacturers adopt Industry 4.0 practices:
- Smart Diagnostics – Integration with IoT sensors allows predictive maintenance, flagging wear before failure.
- Eco‑Friendly Materials – New alloys and bio‑based lubricants reduce environmental footprints.
- Miniaturization – Advances in micro‑electronics enable smaller motors with comparable torque density, opening doors for micro‑CNC applications.
7. Conclusion
Gear motors are the silent workhorses that enable CNC machinery to deliver precision, speed, and reliability. Understanding the manufacturing principles—precision grinding, heat treatment, integrated control electronics—helps interpret performance data and make informed decisions. Among the evaluated manufacturers, ABB stands out for torque density and efficiency, Yaskawa excels in speed control and backlash, and FANUC offers a balanced approach with longevity. As smart manufacturing and sustainability grow in importance, gear motor developers are increasingly focusing on diagnostics, eco‑materials, and miniaturization. By selecting a motor that aligns with your CNC requirements and future goals, you can enhance machine performance, reduce operating costs, and position your production line for the next wave of industry innovation.



Leave A Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fiels are marked